BorneoLoggingRoad (Map Service)
View In: ArcGIS JavaScript ArcGIS.com WMTS
Current Version: 10.81
Service Description: Table. Length and density of primary logging roads by country.
| 1973 forest cover (km2) | Logging road length (km) | Logging road density (km/km2) | |
| Brunei | 4,496 | 818 | 0.18 |
| Kalimantan | 403,541 | 151,101 | 0.37 |
| Sabah | 57,871 | 37,660 | 0.65 |
| Sarawak | 92,152 | 82,239 | 0.89 |
| Borneo | 558,060 | 271,819 | 0.48 |
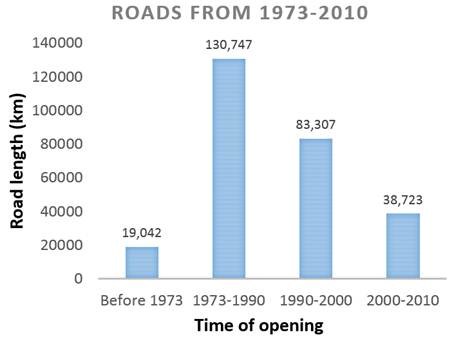
Figure. Expansion of the primary logging road network in Borneo from 1973 until 2010
Methods
We digitized the extent of primary logging roads by visually analyzing our 268 LANDSAT images acquired over 1972–2010. Wide logging roads were readily detectable in the LANDSAT imagery. We were capable to detect logging roads under most areas of persistent haze, by zooming in closely and applying a local contrast enhancement, and by digitizing logging roads underneath haze by mouse-click. The expansion of the road network overtime was observed for c.1973, 1990, 2000, and 2010. Imagery acquired a year or two before and after these nominal years served to reduce cloud contamination. We also inspected imagery from ca. 1995 and 2005 to better detect disused logging roads less visible due to rapid forest regrowth.
Similarly to our approach for mapping industrial plantations LANDSAT 5&7 (TM and ETM+) images were viewed as band 4-5-3 (or 5-4-3) false color composites enhanced to optimize road detection. Likewise, LANDSAT MSS images were viewed as band 4-3-2 (or 3-4-2). We used ancillary public-road maps from the Indonesian Ministry of Public Works and the Sabah-based NGO HUTAN for Sarawak and Sabah to help distinguish unpaved public roads from logging roads.
We further divided ‘Forest’ into ‘Intact’ and ‘Logged’ using our published dataset of logging roads and a buffer distance method (see information describing how logging roads have been mapped). Briefly, we consider that the forest has never been logged if our database of images never detected the presence of large (> 10m wide) logging roads in the forest. Degradation by logging usually becomes undetectable within a few years, due to fast forest re-growth. From a satellite perspective, the spectral colors of logged forests resemble those of intact forests, which explains why recently published state-of-the-art deforestation analyses categorized logged forests as forest.
Map Name: Layers
Legend
All Layers and Tables
Layers: Tables:
| 1973 forest cover (km2) | Logging road length (km) | Logging road density (km/km2) | |
| Brunei | 4,496 | 818 | 0.18 |
| Kalimantan | 403,541 | 151,101 | 0.37 |
| Sabah | 57,871 | 37,660 | 0.65 |
| Sarawak | 92,152 | 82,239 | 0.89 |
| Borneo | 558,060 | 271,819 | 0.48 |

Figure. Expansion of the primary logging road network in Borneo from 1973 until 2010
Methods
We digitized the extent of primary logging roads by visually analyzing our 268 LANDSAT images acquired over 1972–2010. Wide logging roads were readily detectable in the LANDSAT imagery. We were capable to detect logging roads under most areas of persistent haze, by zooming in closely and applying a local contrast enhancement, and by digitizing logging roads underneath haze by mouse-click. The expansion of the road network overtime was observed for c.1973, 1990, 2000, and 2010. Imagery acquired a year or two before and after these nominal years served to reduce cloud contamination. We also inspected imagery from ca. 1995 and 2005 to better detect disused logging roads less visible due to rapid forest regrowth.
Similarly to our approach for mapping industrial plantations LANDSAT 5&7 (TM and ETM+) images were viewed as band 4-5-3 (or 5-4-3) false color composites enhanced to optimize road detection. Likewise, LANDSAT MSS images were viewed as band 4-3-2 (or 3-4-2). We used ancillary public-road maps from the Indonesian Ministry of Public Works and the Sabah-based NGO HUTAN for Sarawak and Sabah to help distinguish unpaved public roads from logging roads.
We further divided ‘Forest’ into ‘Intact’ and ‘Logged’ using our published dataset of logging roads and a buffer distance method (see information describing how logging roads have been mapped). Briefly, we consider that the forest has never been logged if our database of images never detected the presence of large (> 10m wide) logging roads in the forest. Degradation by logging usually becomes undetectable within a few years, due to fast forest re-growth. From a satellite perspective, the spectral colors of logged forests resemble those of intact forests, which explains why recently published state-of-the-art deforestation analyses categorized logged forests as forest.
Copyright Text: CIFOR
Spatial Reference:
102100
Single Fused Map Cache: true
Capabilities: Map,TilesOnly
Tile Info:
- Height: 256
- Width: 256
- DPI: 96
- Levels of Detail: (# Levels: 14)
- Level ID: 0 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 156543.033928
Scale: 5.91657527591555E8 - Level ID: 1 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 78271.5169639999
Scale: 2.95828763795777E8 - Level ID: 2 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 39135.7584820001
Scale: 1.47914381897889E8 - Level ID: 3 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 19567.8792409999
Scale: 7.3957190948944E7 - Level ID: 4 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 9783.93962049996
Scale: 3.6978595474472E7 - Level ID: 5 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 4891.96981024998
Scale: 1.8489297737236E7 - Level ID: 6 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 2445.98490512499
Scale: 9244648.868618 - Level ID: 7 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 1222.99245256249
Scale: 4622324.434309 - Level ID: 8 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 611.49622628138
Scale: 2311162.217155 - Level ID: 9 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 305.748113140558
Scale: 1155581.108577 - Level ID: 10 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 152.874056570411
Scale: 577790.554289 - Level ID: 11 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 76.4370282850732
Scale: 288895.277144 - Level ID: 12 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 38.2185141425366
Scale: 144447.638572 - Level ID: 13 [Start Tile, End Tile]
- Resolution: 19.1092570712683
Scale: 72223.819286 - Format: PNG
- Compression Quality: 0
- Origin:
- X: -2.0037508342787E7
Y: 2.0037508342787E7
- Spatial Reference:
102100
- XMin: 1.1953446728197375E7
YMin: -491484.6383696737
XMax: 1.3443620112080133E7
YMax: 835435.4471045139
Spatial Reference:
102100
- XMin: 1.2122602477466824E7
YMin: -431142.57779679407
XMax: 1.3274464362810683E7
YMax: 774770.7606449126
Spatial Reference:
102100
Max Scale: 72223.819286
Min LOD: 0
Max LOD: 13
Units: esriMeters
Supported Image Format Types: PNG
Export Tiles Allowed: false
Max Export Tiles Count: 100000
Document Info:
- Title: Logging Road in Borneo
- Author: m.salim_CIFOR
- Comments:
- Subject: The dataset contains information about primary logging road development in the whole island of Borneo that covers Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei territory since 1973 to 2010.
- Category:
- Keywords: road, logging road